Generative AI models are revolutionizing the landscape of content creation (and other segments), bringing significant changes to marketing, software development, design, entertainment, and interpersonal communications. These advanced models possess the remarkable ability to generate text and images, including blog posts, program code, poetry, and artwork. Powered by complex machine learning algorithms, these models predict the next word based on previous word sequences or generate images based on textual descriptions. It is crucial for businesses to understand the inner workings of these tools and how they can add value to their operations.
Generative AI, also known as foundation models or large language and image AI models, has introduced a new range of opportunities for professionals and businesses involved in content creation. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Automated Content Generation: Large language and image AI models can automatically generate content such as articles, blog posts, and social media posts. This automation proves invaluable for businesses and professionals who regularly produce content, saving them significant time and effort.
- Improved Content Quality: AI-generated content often exhibits higher quality compared to human-created content. AI models have the ability to learn from vast amounts of data, enabling them to identify patterns that may go unnoticed by humans. As a result, AI-generated content tends to be more accurate and informative.
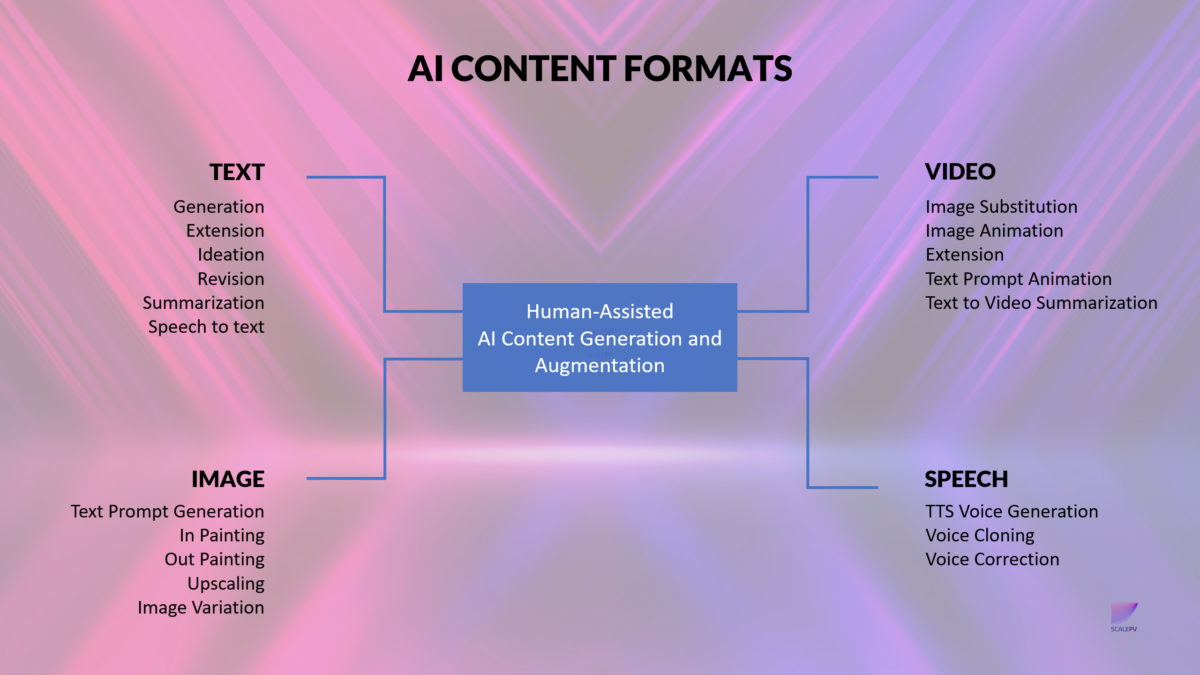
- Increased Content Variety: Generative AI models can generate diverse types of content, including text, images, and videos. This allows businesses and professionals to create a wide range of engaging and captivating content that appeals to a broader audience.
- Personalized Content: AI models excel at generating personalized content tailored to individual user preferences. This capability empowers businesses and professionals to create content that is more likely to resonate with their target audience, leading to higher engagement and sharing.
- Easier Access to Content: Large language models make text the interface for content generation and consumption, offering a widely accessible and user-friendly approach to everybody.
- Increased Productivity: Advanced AI models like GPT-4 can process vast amounts of information in a matter of minutes, a task that would otherwise take months for a team of individuals. This significantly improves productivity and efficiency in content creation workflows.
However, it’s important to note that while AI models can mimic human efforts in creative work, they still exhibit certain limitations. The generated content is highly dependent on the input prompts provided to the model, and multiple iterations may be required to achieve the desired outcome. Human involvement is still crucial at the beginning and end of the content generation process, with human evaluation and editing playing a vital role in refining the output.
Let’s delve deeper into the concept of generative AI.
Generative AI has already demonstrated impressive capabilities in producing text and images across various domains such as blog posts, program code, poetry, and artwork. The underlying software relies on complex machine learning models that predict the next word based on previous word sequences or generate images based on textual descriptions. These models, often referred to as large language models (LLMs), originated at Google Brain in 2017, initially used for word translation while preserving context. Since then, large language models and text-to-image models have proliferated at leading tech firms such as Google (BARD and LaMDA), Facebook (OPT-175B, BlenderBot), and OpenAI (GPT-4 for text, DALL-E2 for images, and Whisper for speech). Online communities like Midjourney, companies like Stability AI with Stable Diffusion image generator, and open-source providers like HuggingFace have also contributed to the development and availability of generative models.
However, the training of these models requires massive amounts of data and computing power, making them predominantly accessible to major tech companies. For instance, GPT-3, one of the notable models, underwent training with 45 terabytes of data and employs 175 billion parameters for predictions, amounting to a training cost of $12 million. Models like Wu Dao 2.0 in China boast an impressive 1.75 trillion parameters. These training requirements exceed the capabilities of most companies lacking extensive data centers and cloud computing resources.
Nevertheless, once a generative model is trained, it can be fine-tuned with less data for specific content domains, enabling specialized models for various purposes. For example, there are domain-specific models like BioBERT for biomedical content and Legal-BERT for legal content. NVIDIA’s BioNeMo provides a framework for training and deploying large language models at supercomputing scale for generative chemistry, proteomics, and DNA/RNA applications. OpenAI has found that even as few as 100 specific examples of domain-specific data can significantly enhance the accuracy and relevance of GPT-4’s outputs and is what our services use to generate GPT-4 integrations to company data, generating their internal ChatGPTs.
To effectively utilize generative AI, human involvement is necessary at both the beginning and end of the content creation process. Humans provide the initial prompts for the generative models, and the generated content requires careful evaluation and editing to ensure quality and alignment with the intended purpose. While generative AI offers immense potential, it is important to understand its limitations and the need for human expertise and oversight.
In summary, generative AI models are reshaping the creative work landscape, offering automated content generation, improved content quality, increased content variety, personalized content, and enhanced productivity. However, human involvement remains crucial, and the technology has its limitations. By harnessing the power of generative AI while maintaining human oversight, businesses can unlock new possibilities and achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness in content creation.

